TEMPLE ARCHITECTURE OF INDIA
ALL STYLE

NAGARA STYLE- NORTH INDIA
Nagara temples have two distinct features :
- In plan, the temple is a square with a number of graduated projections in the middle of each side giving a cruciform shape with a number of re-entrant angles on each side.
- In elevation, a Sikhara, i.e., tower gradually inclines inwards in a convex curve.
PRATHIHARAS- UJJAIN (8TH – 9TH CENTURIES AD)
• Mahakaleshwar temple, one of the 12 Jyotirlingas of India,
• Kal Bhairava temple, finds a mention in the Skanda Purana, and
• Mangalnath temple, regarded as the birthplace of Mars, according to the Matsya Purana.PALAS- BENGAL AND BIHAR (8th -13TH CENTURIES AD)
• flourished in Bengal and Bihar under the Pala and the Sena rulers.
• Nalanda was its most active centre, whose influence was spread to Nepal, Myanmar and even Indonesia.
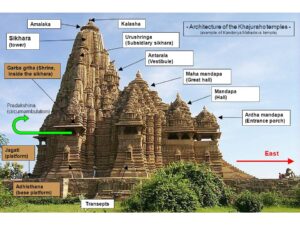
CHANDELAS- BUNDELKHAND (10TH -11TH CEN AD)
• Khajuraho justly famous for their graceful contours anderotic sculptures.
• These 22 temples (out of the original 85) are regarded as one of world’s greatest artistic wonders.
• Khajuraho Temples were built within a short period of hundred years from 950-1050 A.D.
• Kendriya Mahadev temple is the largest and most beautiful of the Khajuraho Temples.
• Shiva Temple at Visvanath and Vishnu Temple at Chaturbhunj are other important temples at Khajuraho.DRAVIDIAN STYLE – SOUTH INDIA
Dravidian style temples consist almost invariably of the four following parts:
DRAVID SYTLE


- The principal part, the temple itself, is called the Vimana (or Vimanam). It is always square in plan and surmounted by a pyramidal roof of one or more stories; it contains the cell where the image of the god is placed.
- The porches or Mandapas, which always cover and precede the door leading to the cell.
- Gate-pyramids or Gopurams, which are the principal features in the quadrangular enclosures that surround the more notable temples.
- Pillared halls or Chaultris—properly Chawadis — used for various purposes, and which are the invariable accompaniments of these temples.
VESARA STYLE – DECCAN
VERSA

• Vesara is a combination of NAGARA & DRAVIDIAN temple styles
• Hoysala temples at Belur, Halebidu and Somnathpura are supreme examples of this style