GUPTA Empire, Period, Administration, Literature, Arts
Gupta Age
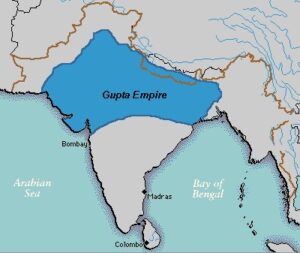
- Gupta age regard as “golden period ” of HINDUISM
- According to vishupuran gupta belongs to “Vaishya”.
- Founder –Shree Gupta (Adhiraj).
- SriGupta (240-280 AD) was ruling a small Hindu kingdom called Magadha from Vaishya community near Ganga river, a prayag based feudatory of Kushanas.
- His son Ghatotkacha (280 – 319 AD) became the successor of Sri Gupta.
Chandragupta-I (319-335 A.D.)
- Son of Ghatotkacha
- He started the Guptan era i.e. 320 A.D.
- He strengthened his kingdom by matrimonial alliance with the powerful family of Lichchhavis who were the rulers of Mithila.
- His marriage to Lichchhvi princess Kumaradevi, brought an enormous power, resources and prestige. He took advantage of the situation and occupied the whole of fertile Gangetic Valley.
- After the marriage he issued the special type of coins called ―Chandragupta I-kumaradevi type‖.
- He acquired the title of Maharajadhiraj
- Chandragupta-I was able to establish his authority over Magadha, Prayaga & Saketa.
Samudragupta (335-375 A.D.)
- Also called “Indian-Nepolain”
- Samudragupta was the greatest king of Gupta dynasty
- In Allahabad inscription Samudragupta describes him as the “hero of hundred battles”.
- The Allahabad pillar inscription composed by Harisena, his court poet.
- He was a great patron of art, adopted the title of ‘Kaviraja’.
Chandragupta II (380-413 A.D.)
- He was also called “Vikramaditya” & made Ujjain as its second capital.
- First ruler issued silver coin in the memory of victory over Sakas.
- He was also a man of art and culture, his court at Ujjain was adorned by ‘Navratna’-
- Kalidas – poet
- Amarsinha – lexicographer
- Dhanvantari- Doctor
- Vetal batt – magician
- Vaharmihir-Astronomer
- Varachi –grammerian
- Shanka –Architect
- Harisena – court poet
- Kshapank- Astrologer
- Chinese pilgrim Fa-Hien visited India during his regime.
Kumargupta-I 415-455 AD
- He assumed the title of Mahendraditya.
- Founded the Nalanda University.
- He was a worshipper of Lord Kartikeya (son of Lord Shiva.)
- Towards the end of his reign, the Gupta Empire was threatened from the North by the Huns, which was temporarily checked by his son Skandagupta
Skandagupta : 455-467 AD
- He restored the Sudarshana Lake.
- Skandagupta repulsed the ferocious Hunas twice,this heroic feat entitled him to assume the title of Vikramaditya.
Administration
- Contrast to the Mauryans
- Council of minister existed
- Several post become hereditary
- The empire was divided into
- Bhukti= provinces headed by Uparika(viceroy)
- Vishayas=District headed by Vishpati
- Peth =sub district
- Gramika or Mahattar =village.
- Not maintain vast bureaucracy
- Kumaramatyas was important post appointed by the King.
- A large part of kingdom was administered by Feudatories.
- Important development of feudal development in administration was the grant of fiscal and administrative concession to the priests and administrators.
- First time civil and criminal laws were defined and demarcated.
- Divinity in kinship
- Large number of silver coin = Rupayaka and Gold coin= Dinnar were issued.
Social condition
- Aryans pattern of society @varna system
- Tax free land granted to the Brahmans
- Land granted for religious function called Agarhara(free of tax)
- Mother goddess were worshiped but postion of women was lower
- The first example of sati came from Eran(MP) of 510 AD
- Untouchability was increased
Religion
- Bhagvat geeta written during this time
- Decline in Buddhism
- Idol worshiped became common
- Vishnu temple at Deogarh(near Jhansi)
- Brick temple Bhitragaon (Kanpur) belongs to Gupta period
Art
- A number of temples, sculpture etc. were developed in this period.
- Samudragupta were present on his coins playing veena(lute)
- Mathura school was developed during the period of Gupta
- Buddha sitting in his dharma chakra mudra at Sarnath belongs to gupta period
- Buddha image of bamiyan belongs to this age (destroyed by the Tabliban)
- Ajanta and Bagh painting are belongs to tis age related to the Buddhist art
- Image of vishu ,shiva and other hindu gods featured for the first time in this period.
Literature
- Number of literature works were written in this period
- Kalidas–
- ABhigyanam Shakuntalam
- Ritusamhar
- Meghdutam
- Kumar sambhavam
- Malvikagnimitram
- Raghuvansh
- Sudrak-
- Mirchkatikam
- Bharavi
- Dandin
- Bhasa- written 11 plays most famous among them was= Charudatta (Rekha wali utsav movie lolz)
- Vishakdatt-
- Mudra rakshas
- Devi Chandragupta
- Vishnu sharma
- Panchtantra
- Hitobdesh
- Development of Sanskrit based on Panini and Patanjali
- Most important was AMARAKOSH written by Amarsimha
- Ramayana and Mahabharata also completed by the 4th century
Science and technology
- Highly developed
- Science of transplantation of internal organs was known to the Gupta period
- Sushutra is known as father of the surgery .highly specialized instruments were used
- Danvantri was famous Aurvedacharya
- Arya bhatta was famous Mathematician wrote “Arybhatiya” and “Surya Samhita”.
- He also calculated the value of pie use of algebra and sine angle
- He discovered the cause of solar and lunar eclipse
- Vaharmihir written “panchsidhantika” and “Brihatsamhita”
- Bramhagupta was famous mathemacian
- Vagabhatta was famous physicaian
Note– Court language was Sanskrit