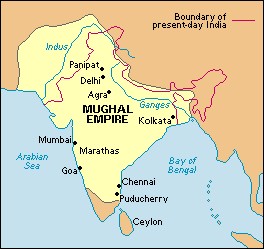
MUGHAL EMPIRE OR Mughal period
 Zahir-ud-din Muhammad Babur
Zahir-ud-din Muhammad Babur
- The foundation of the Mughal rule in India was laid by Babur in 1526.
- He was a descendant of Timur (from the side of his father) and Chengiz Khan (from the side of his mother).
- Babur was invited by Daulat Kahna Lodi and Alam Khan Lodi against Ibrahim Lodi
- Babur defeated Ibrahim Lodhi in the first battle of Panipat on April 21, 1526 and established Mughal dynasty.
- Babur successes due to use of Ottoman(rumi) device in war.
- In 1527, he defeated Rana Sanga of Mewar at Khanwa.
- In 1528, he defeated Medini Rai of Chaneri at Chanderi.
- In 1529, he defeated Muhammad Lodhi (uncle of Ibrahim Lodhi) at Ghaghra.
- In 1530, he died at Agra. His tomb is at Lahore. The tomb of only two Mughal emperors are outside India i.e. Babur and Bahadur Shah Zafar
- He was the first to use gunpowder and artillery in India.
- Two gun masters Mustafa and Ustad Ali were in his army
- He wrote his autobiography Tuzuk-i-Baburi in Turki .
MUGHAL EMPIRE
Nasir-ud-din Muhammad Humayun (1530-40 and 1555-56)
- He was the son of Babur and ascended the throne in 1530. His succession was challenged by his brothers Kamran, Hindal and Askari along with the Afghans.
- In 1532 he established Tabl-e-adl at Agra.
- He fought two battles against Sher Shah at Chausa (1539) and at Kannauj/Bilgram (1540) and was completely defeated by him.
- He escaped to Iran where he passed 12 years of his life in exile.
- After Sher Shah‘s death Humayun invaded India in 1555 and defeated his brothers the Afghans. He once again became the ruler of India.
- He died while climbing down the stairs of his library (at Din Panah) in 1556 and was buried in Delhi.
- His sister, Gulbadan Begum wrote his biography Humayunama.
- He built Din Panah at Delhi as his second capital.
The Afgan interlude –Sur empire(1540-1556 AD)
Sher Shah Suri
- His original name was Farid he was born in Hoshiyarpur Punjab
- Mohammad Shah Nuhani independent ruler of Bihar gave him that Title “Sher Shah Suri”.
- In 1539 in the battle of chausa near Buxar Mughal were defeated by Suri
- As an emperor, he conquested Malwa (1542), Ranthambhor (1542), Raisin (1543), Rajputana annexation of Marwar (1542), Chittor (1544) & Kalinjar (1545).
- He died in 1545 while conquesting Kalinjar
- He issued the coin called Rupiah and fixed standard weights and measures all over the empire.
- Abbas Khan Sarwani was historian wrote Tarik-e-Shershahi
- His hindu minister Hemu became powerful and adopted the title of “Vikramditya”.
- Hemu was defeated by Akbar in the 2nd battle of Panipat
Administration
- Sher shah build sarai(inn) at a distance of two kos (8km)
- He also improved communications by building several highways. He built the Grand Trunk Road (G.T. Road), which runs from chhitgaon to Kabul
- Improved revenue system adapting “zabti-i-har-sala”
- Land was measured usig Gaz—i-shikandari.
- According to Abul Fazal the empire of Sher Shah was divided into 63 sarkars or districts
Jalaluddin Muhammad Akbar(1556-1606 AD)
- Born in Amarkot in 1542
- He became king in age of 14
- The Mughal Afgan force meet at panipath on 5 November 1556(second battle of panipath)
- Mughals defeated Hemu
- Akbar built Fatehpur Sikri, Agra Fort, Lahore Fort and Allahabad Fort and Humayun‘s Tomb at Delhi.
- Fatehpur Sikri, place near Agra-it said that Akbar had no son for a long time. Sheikh Salim Chisti, a Sufi saint blessed Akbar with a son who was named Salim/Sheikho Baba (Jahangir). In honour of Salim Chisti, Akbar Shifted his court from Agra to Fatehpur Sikri.
- Tulsidas (author of Ramcharitmanas) also lived during Akbar‘s period.
- When Akbar died, he was buried at Sikandara near Agra.
Policy of expansion
- Between 1556 to 1576 the Mughal territory expanded rapidly
- Akbar conquered Ajmer,Malwa,(defeated bazbahadur in 1561)
- Chittor in 1568
- He defeated Rana Pratap of Mewar in battle of haldighati in 1576
Religious policy
- Respect to ulemas
- Iin 1562 after having matrimonial alliance with rajputs akbar followed liberal measures
- In 1563 Pilgrim tax was abolished
- In 1582 Akbar inaugurated Tauhid-i-ilahi also know as din-i-ilahi
Revenue system
- Revenue system known as Todarmal system or Zabti system
- Zabti system salient feature-
- Measurement of land
- Classification of land
- Fixation of rates
Mansabdari system
- Every office assigned a rank called mansab
- The rank were divided into two Zat and Sawar
- Each Mughal officer was assigned a mansab (rank), there were 66 categories of Mansabdars
Noor –ud-din Muhammad Jahangir (1605-27)
- Salim, son of Akbar, came to the throne after Akbar‘s death in 1605
- He established Zanjir-i-Adal (i.e. Chain of Justice) at Agra Fort for the seekers of royal justice.
- In 1611, Jahangir married Mihar-un-nisa, widow of Sher Afghan, a Persian nobleman who was sent on expedition to Bengal. Later on she was given the title Nurjahan.
- Nurjahan excercised tremendous influence over the state affairs. She was made the official Padshah Begum.
- Jahangir issued coins jointly in Jurjahan‘s name and his own.
- Jahangir also married Jodha Bai of Marwar.
- In 1608, Captain William Hawkins, a representative of East India Company came to Jahangir‘s court. In 1615 Sir Thomas Roe, an ambassador of King James I of England also came to his court.He granted permission to the English to establish a trading port at Surat.
- His reign was marked by several revolts. His son Khusrau, who received patronage of 5th Sikh Guru Arjun Dev, revolted against Jahangir (1605). Arjun Dev was later sentenced to death for his blessing to the rebel prince (1606).
- He wrote his memories Tuzuk-i-Jahangiri in Persian.
- He was buried in Lahore.
Shah Jahan(1627-1658 AD)
- His real name was Khurram, he was born to Jodha Bai (daughter of Raja Jagat Singh).
- Three years after his accession, his beloved wife Mumtaj Mahal (original name- Arzumand Bano) died in 1631. To perpetuate her memory he built the Taj Mahal at Agra in 1632-53.
- He continued applying tika (tilak) on the fore-head
- He introduced the Char-Taslim in the court
- In addition to Jahangir‘s empire, Nizam Shahi‘s dynasty of Ahmadnagar was brought under Mughal control (1633) by Shahjahan.
- Shahjahan‘s reign is described by French traveler Bernier and Tavernier and the Italian traveler Nicoli Manucci. Peter Mundi described the famine that occurred during Shahjahan‘s time.
- The Red Fort, Jama Masjid and Taj Mahal are some of the magnificent structures built during his reign.
- Shahjahan‘s failing health set off the war of succession among his four sons in 1657.
- Aurangzeb emerged the victor who crowned himself in July 1658. Shahjahan was imprisoned by his son Aurangzeb in the Agra Fort where he died in captivity in 1666. He was buried at Taj (Agra).
Aurangzeb (1658-1707 AD)
- The war of succession took place in the later stage of the Shah Jahan reign.
- His four sons Dara Shikoa, Aurangzeb, Shah Shuja and Murad were in the state of war for the throne.
- His daughters also supported one son or the other in the tussle for throne Janah Ara supported Dara. Roshan Ara supported Aurangzeb. Guhara supported Murad.
- Aurangzeb was coroneted twice, he was the only Mughal king to be coroneted twice
- Barnier was the foreign visitor who saw the public disgrace of Dara after he was finally deafeated in war at Deorai.
- During the first 23 years of the rule (1658-81) Aurangazeb concentrated on North India. During this period the Marathas under Shivaji rose to power and were a force to reckon with.
- Highest numbers of Hindu Mansabdars were there in the service of Mughals during the reign of Aurangzeb.
- Aurangzeb captured Guru Teg Bahadur, the 9th Guru of Sikhs in 1675 and executed him when he refused to embrace Islam.
- The 10th and last Sikh Guru, Guru Gobind Singh, son of Guru Teg Bahadur, organized his followers into militant force called Khalsa to avenge the murder of his father.
- Guru Gobind Singh was, however murdered in 1708 by an Afghan in Deccan. Banda Bahadur, the militant successor of Guru Gobind Singh continued the war against Mughals.
Religious policy of Aurangzeb:
- He was called Zindapir or living saint
- Muhatasibs were appointed for regulation of moral conduct of the subjects
- He forbade singing in the court, but allowed musical instruments. He himself played Veena
- He ended Jhoraka darshan started by Akbar
- He ordered that no new Hindu temples were to be built. Old temples were allowed to be repaired
- The Viswanath temple at Kashi and the Keshav Rai temple of Bir Singh Bundela at Mathura were destroyed
- In 1679 he re-imposed Jaziya tax
Mughal Administration:
Central administration:
- Wakil: He was initially the prime minister, however later became revenue advisor only
- Mir Bakshi: He was the head of military department
Provincial administration:
- The empire was divided into provinces or Subas
- In 1580, Akbar divided the empire into 12 provinces. The number of provinces became 15 towards the end of his reign.
- In Jahangir‘s reign the number of provinces rose to 17 and further in Aurangzeb‘s reign to 21
- The Nazim or Subedar was the head of provinces
Local administration:
- The provinces were divided into Sarkars, which were sub divide into Parganas and further into villages
Mughal Culture
- Jahangir‘s reign was the apex culmination for the Mughal painting while that of Shah Jahan was the apex culmination for architecture.
- Babur built two mosques, one at Kabulibagh in Panipat and the other at Sambhal in Rohilakhand.
- Humayun‘s tomb was built by his widow Haji Banu Begum.
- The Mariam‘s palace, Diwan-i-Aam, Diwan-i-Khas at Sikri are Indian in their plan.
- Buland Darwaja (built after Gujarat victory), formed the main entrance to Fatehpur Sikri. By Akbar
- Salim Chisti‘s tomb (redone in Marble by Jahangir) is the first Mughal building in pure marble). Palace of Birbal and palace of Tansen are also inside the Fatehpur Sikri.
- Akbar also began to build his own tomb at Sikandara which was later completed by Jahangir.
- The architecture of Fatehpur Sikri is known as Epic in red sand stone.
- Nurjahan built Itimad-ud-daula or Mirza Ghiyas Beg‘s marble tomb at Agra, which is noticable for the first use of Pietra Dura (floral designs made up of semiprecious stones) technique.
- Jahangir built Moti Masjid in Lahore and his mausoleum at Shahdara (Lahore).
- Some of the important buildings built by Shahajahan at Agra are Moti Masjid (only Mosque of marble). Khaas Mahal, Mussmman Burz (Jasmine Palace where he spent his last year in captivity) etc.
- He laid the foundations of Shahjahanabad in 1637 where he built the Red Fort and Takht-i-Taus (Peacock throne).
- Only building by Aurangzeb in the Red Fort is Moti Masjid.
- Only monument associated with Aurangzeb is Bibi ka Makbara which is the tomb of his wife Rabbiaud-daura in Aurangabad.
- Aurangzeb also built the Badshahi Masjid in Lahore.
- Humayun had taken into his service two master painter Mir Syed Ali and Abdus Samad.
- Daswant and Basawan were two famous painters of Akbar‘s court.
- Abdul Hassan, Ustad Mansur and Bishandas were three famous painters of Mughal
Literature
- Akbar Nama–Abul Fazl
- Tobaqat-i-Akbari–Khwajah Nazamuddin Ahmad Baksh
- Iqbalnama-i-Jahangiri—Muhammad Khan
- Ain-i-Akbari –Abul Fazl
- Padshah Namah– Abdul Hamid Lahori
- Shahjahan Namah– Muhammad Salih
- Sirr-i-Akbar– Dara Shikoh
- Safinat-ul-Auliya — Dara Shikoh
- Majma-ul-Bahrain — Dara Shikoh
- Raqqat-e-Alamgiri – AurangzebJahangir‘s court.