DELHI SULTANATE
Delhi Sultanate(1206 to 1526 AD)
- After the assassination of Muhammad Ghori, Qutubuddin Aibek got the control over Delhi
- This period can be divided into 5 distinct periods viz.
DELHI SULTANATE
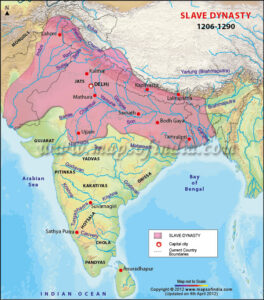
- The Slave Dynasty (1206-90)
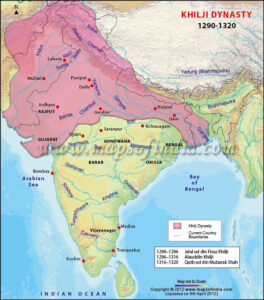
- The Khilji Dynasty (1290-1320)
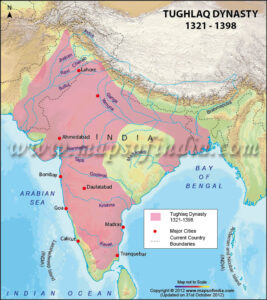
- The Tughlaq Dynasty (1320-1414)
- The Sayyid Dynasty (1414-51)
- The Lodhi Dynasty (1451-1526).
The Slave or illbari Dynasty (1206-1290 AD)
- Its called illbari dynasty because all ruler except Aibak belonged to IIbari tribe of turks
Qutubuddin Aibak (1206-10)
- A Turkish slave by origin, he was purchased by Mohammad Ghori who later made him his Governor.
- After the death of Ghori, Aibak became the master of Hindustan and founded the Slave Dynasty in 1206.
- The capital during his reign was not Delhi but Lahore.
- For his generosity, he was given the title of Lakh Bakhsh (giver of lakhs).
- He died in 1210 while playing Chaugan or Polo.
- Aibak was great patron of learning and patronized writers like Hasan-un-Nizami, author of ‗Taj-ul- Massir‘ and Fakhruddin, author of ‗Tarikh-i-Mubarak Shahi‘.
Aram Shah (1210)
- He was the son of Aibak, who was defeated by Illtutmish in the battle of Jud
Shamsuddin Illtutmish (1210-36)
- He was a slave of Qutubuddin Aibak of Mamluke tribe and occupied the throne of Delhi in 1211.
- Illtutmish began his career as Sar-e Jandhar or royal bodyguard.
- He was a very capable ruler and is regarded as the ‗real founder of the Delhi Sultanate‘.
- He made Delhi the capital in place of Lahore.
- He saved Delhi Sultanate from the attack of Chengiz Khan, the Mongol leader, by refusing shelter to Khwarizm Shah, whom Chengiz was chasing.
- He introduced the silver coin (tanka) and the copper coin (jital).
- He organized the Iqta System and introduced reforms in civil administration and army, which was now centrally paid and recruited.
- He set up an official nobility of slaves known as Chahalgani/ Chalisa (group of forty).
- He completed the construction of Qutub Minar which was started by Aibak.
- He patronized Minhaj-us-Siraj, author of ‗Tabaqat-i-Nasiri‘.
Ruknuddin : (1236 AD)
- He was son of Illtutmish and was crowned by her mother, Shah Turkan, after death of Illtutmish.
- He was deposed by Razia, daughter of Illtutmish.
Razia Sultana: (1236 – 40 AD)
- Iltutmish had nominated his daughter Razia as the successor, the nobles placed Ruknuddin Feroz on the throne.
- She was the first and only Muslim lady who ever ruled India.
- She use to rule without the veil
- She further offended the nobles by her preference for an Abyssian slave Yakut.
- The wazir of Illtutmish Junnaidi revolted against her but was defeated.
- There was a serious rebellion in Bhatinda, Altunia, governor of Bhatinda refused to accept suzerainity of Razia. Razia accompanied by Yakut marched against Altunia.
- However, Altunia got Yakut murdered and imprisoned Razia.
- Subsequently, Razia was married to Altunia and both of them marched towards Delhi as nobles in Delhi raised Bahram Shah (3rd son of Illtutmish) to throne.
- In 1240 AD, Razia became the victim of a conspiracy and was assassinated near Kaithal (Haryana).
Bahram Shah: (1240-42)
- Iltutamish‘s third son Bahram Shah was put on throne by powerful Turkish council Chalisa.
- He was killed by Turkish nobles.
Allauddin Masud Shah: (1242-46)
- He was son of Ruknuddin Feroz.
- He was disposed after Balban and Nasiruddin Mahmud‘s Mother, Malika-e-Jahan, conspired against him and established Nasiruddin Mahamud as the new Sultan.
Nasiruddin Mahmud (1246-66)
- He was the eldest son of Illtutmish.
- Minaj-us-Siraj has dedicated his book Tabaquat-i-Nasiri to him
Ghiyasuddin Balban (1266-87)
- After the death of Nasiruddin; Balban ascended the throne in 1266.
- He broke the power of Chalisa and restored the prestige of the crown. He made kingship a serious profession.
- The Persian court model influenced Balban‘s conception of Kingship. He took up the title of Zil-i-Ilahi (Shadow of God).
- He introduced Sijda (prostration before the monarch) and Paibos (kissing the feet of monarch) as the normal forms of salutation.
- Divine right of the king was emphasized by calling himself Zil-i-Ilahi.
- He gave great emphasis on justice and maintaining law and order.
- He established the military department Diwan-i-Arz.
- In his last days he overlooked Sultanate affairs due to death of his eldest and most loving son, Muhammad, and rebellion by his closest and most loved slave, Tughril. Muhammad died fighting Mongolians in 1285 and Tughril was captured and beheaded.
Kaiqubad: (1287-90)
- He was the grandson of Balban was established on the throne by Fakruddin, the Kotwal of Delhi
- But Kaiqubad was killed by nobles Kaimur
- He was the minor son of Kaiqubad who came to throne at an age of 3
- He was the last Illbari ruler
- The Khalji nobles revolted against him and he was killed within three months
The Khalji dynasty (1290-1320 A.D.)
Jallauddin Khalji(1290-96 AD)
- Jalaluddin Khilji founded the Khilji dynasty.
- He was a liberal ruler and adopted the policy of religious toleration
- His son-in-law and nephew was Allauddin Khalji
Allauddin Khalji(1296-1316 AD)
- He was the first Turkish Sultan of Delhi who separated religion from politics. He proclaimed Kingship knows no Kinship’.
- During the reign of Jallauddin Khalji, he was the governor of Kara
- He adopted the title Sikander-e-Saini or the second Alexander
- Alauddin annexed Gujarat (1298), Ranthambhor (1301), Mewar (1303), Malwa (1305), Jalor (1311).
- In Deccan, Aluddin‘s army led by Malik Kafur defeated Ram Chandra (Yadava ruler of Devagiri), Pratap Rudradeva (Kakatiyaruler of Warangal), Vir Ballal III (Hoyasala ruler of Dwarsamudra) and Vir Pandya (Pandya ruler of Madurai).
- Malik Kafur was awarded the title Malik Naib.
Administrative and Market reforms
- In order to avoid the problems created by the nobles. Alauddin issued 4 ordinances.
- The 1st ordinance aimed at confiscation of the religious endowments and free grants of lands.
- The 2nd ordinance Alauddin reorganized the spy system.
- The 3rd ordinance prohibited the use of wine.
- The 4th ordinance issued by Alauddin laid down that nobles should not have convivial parties and they should not inter-marry without his permission.
- He introduced the system of Dagh (the branding of horse) and Chehra (descriptive roll of soldiers).
- Alauddin ordered that all land was to be measured and then they share of state was to be fixed.
- The post of special officer called Mustakharaj was created for the purpose of collection of revenue.
- Alauddin sought to fix cost of all commodities.
- All goods for sale were brought to an open market called Sara-i-Adal.
- Many forts were built by him and the most important of them was Alai fort. He also constructed the Alai Darwaja, the entrance gate of Qutub Minar. He also built the Palace of thousand Pillars called Hazar Sutun.
- He was a patron of art and learning. Amir Khusrau, the poet-musician was his favorite court poet.
- In 1316, after death of Alauddin, Malik Kafur seized the throne.
- Before Kafur died, he nominated Shihabuddin (Alauddin‘s 6 year old prince) as King but imprisoned eldest prince Mubarak Khan.
- Kafur was killed by the loyalists of the royal family of Alauddin. Shiabuddin Umar.
Shiabuddin Umar (1316)
- He was the minor son of Jhitaipali who was raised to throne after the death of Allauddin.
- He became victim of the court politics and was later blinded.
Mubarak Khalji (1316-20)
- He released 18,000 prisoners
- He reversed all the administrative and market reforms of Allauddin Khalji.
- During his time Devgiri was annexed.
The Tuglaq Dynasty(1321-1398 AD)
Ghiyasuddin Tughlaq(1320-1325 AD)
- Ghazi Malik or Ghiyasuddin Tughlaq of Qaurana tribe was the founder of Tughlaq dynasty.
- He was the governor of Dipalpur before coming to power as Sultan
- He died in the collapse of the victory pavilion near Delhi
Mohammad Bin Tughlaq (1325-51)
- Prince Jauna, son of Ghiyasuddin Tughlaq ascended the throne in 1325.
- He gained the title Ulugh Khan, he was most educated of all the Sultans of the Delhi Sultanate
- He created a department Diwan-e-Amir-e-Kohi for the improvement of the agriculture
- He distributed Sondhar i.e. agriculture loans advanced for extension of agriculture of barren land
- He encouraged cash crops in place of cereals
Feroz Shah Tughlaq (1351-88)
- He was a cousin of Mohammad-bin Tughlaq.
- He adopted the policy of appeasement with the nobility, the army and theologians
- The new system of taxation was according to quran. Four kinds of taxes sanctioned by the Quran were imposed and those were Kharaj, Zakat, Jizya and Khams. Kharaj was the land tax, which was equal to 1/10 of the produce of the land, Zakat was 2% tax on property, Jizya was levied on non-Muslims and Khams was 1/5 of the booty captured during war.
- Firoz tried to ban practices, which the orthodox theologians considered non Islamic. Thus he prohibited the practice of Muslim women going out to worship at graves of saints and erased paintings from the palace.
- It was during the time of Firoz that Jizya became a separate tax.
- In order to encourage agriculture, the Sulatan paid a lot of attention to irrigation. Firoz repaired a number of canals and imposed Haque-i-Sharb or water tax
- He was a great builder as well; to his credit are cities of Fatehabad, Hisar, Jaunpur and Firozabad.
- The two pillars of Ashoka, one from Topra (Haryana) and other from Meerut (U.P.) were brought to Delhi.
- The Sultan established at Delhi, a hospital described as Dar-ul-Shifa.
- A new department of Diwan-i-Khairat was set up to make provisions for marriage of poor girls.
- However his rule is marked by peace and tranquility and credit for it goes to his Prime Minister Khan-i- Jahan Maqbul.
- He died in 1388.
The Sayyaid dynasty(1414-1451 AD)
- Khizr Khan (1414-21) founder of the dynasty.
- Mubarak Shah (1421-34).
- Muhammad Shah (1434-43).
- Alam Shah (1443-51)–He was the last Sayyid king descended in favour of Bahlol Lodhi and he retired. Thus began the Lodhi dynasty.
The Lodi Dynasty (1451-1526 AD)
 Bahlol Lodhi : (1451-88)
Bahlol Lodhi : (1451-88)
- Bahlol Lodhi was one of the Afghan sardars who established himself in Punjab after the invasion of Timur.
- He founded the Lodhi dynasty.
- Jaunpur was annexed into Delhi Sultanat during his reign
Sikandar Lodhi : (1489-1517)
- Sikandar Lodi was the son of Bahlol Lodhi who conquered Bihar and Western Bengal.
- Agra city was founded by him.
- Sikandar was a fanatical Muslim and he broke the sacred images of the Jwalamukhi Temple at Nagar Kot and ordered the temples of Mathura to be destroyed.
- He reimposed Jaziya tax on non muslims
- He use to write poems with the pen name ―Gulrukhi‖
- He took a keen interest in the development of agriculture. He introduced the Gaz-i-Sikandari (Sikandar‘s yard) of 32 digits for measuring cultivated fields.
Ibrahim Lodhi (1517-26)
- He was the last king of the Lodhi dynasty and the last Sultan of Delhi.
- He was the son of Sikandar Lodhi.
- At last Daulat Khan Lodhi, the governor of Punja invited Babur to overthrow Ibrahim Lodhi.
- Babur accepted the offer and inflicted a crushing defeat on Ibrahim Lodhi in the first battle of Panipat in 1526.
- He was the only Sultan who died in battle field.
Administration of DELHI SULTANATE period
- There were four pillars of the state i.e.:
- Diwan-i-Wizarat or finance department
- Diwan-i-Risalat or department of religious matters and appeals
- Diwan-i-Arz or department of military affairs
- Diwan-i-Insha or department of royal correspondence
Art and culture development of DELHI SULTANATE period
- The new features brought by the Turkish conquerors were :
- The dome
- The lofty towers
- The true arch unsupported by beam
- The vault
- Qutub-ud-din Aibak build two great mosques one at delhi know as “Quwat-ul-islam” and other at Ajmer called “Dhai din ka Jophra”.
- Qutub-ud-din is also credited to have begun the construction of the world famous Qutub-Minar,the tallest minar in the world of the memory of the memory of sufi saint Qutubud-ud-din-Bakhtiyar kaki .
- Ala-ud-din Khilji Built the new city of Delhi called Siri.he also constructed “Alai Darwaja”.and big tank “Hauz khas”
- Firoz shah tuglaq build Firozabad,Jaunpur& Hissar he brought Ashoks pillar from AMbala & Meerut to Delhi.
- Amir khusro called Tut-e-hind he served from the court of Balban to Muhamad-Bin tuglaq.
- Credit of use Tabla &sitar goes to amir khusro.
Literature OF DELHI SULTANATE period
- Al-baruni ,who visited India in the company of Mahmud Gazni ,his book “Tarik-e-Hind” is an important source of history
- Firoz-Shah-Tuglaq wrote a book “farhut Firoz shahi”